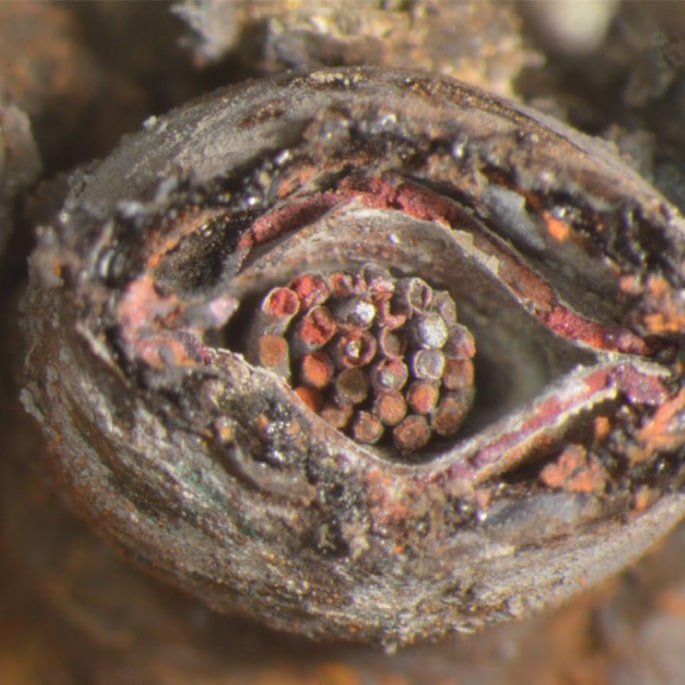
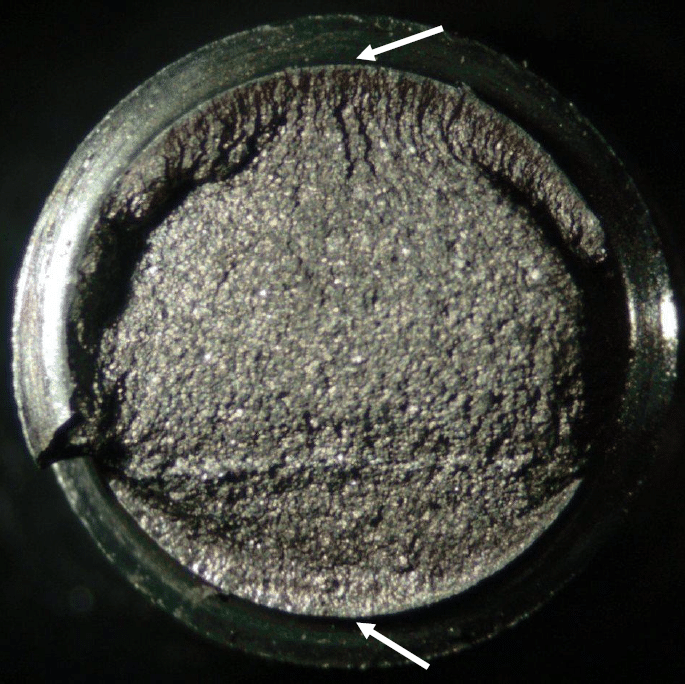
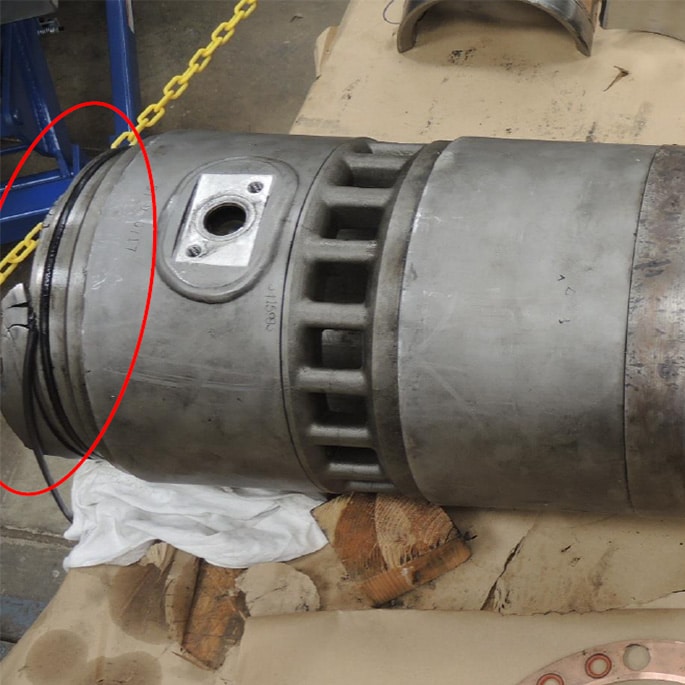
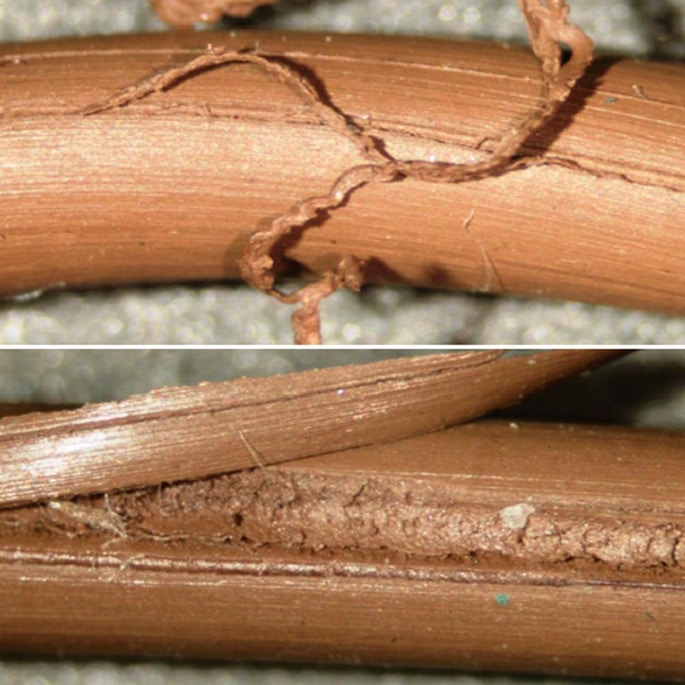
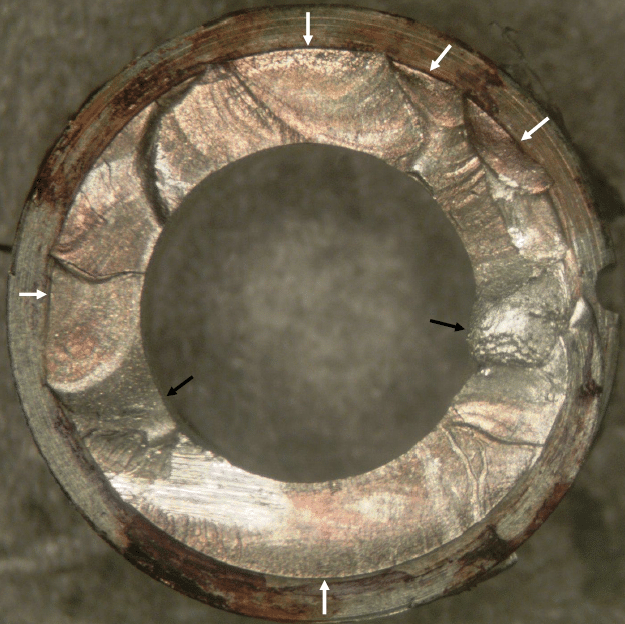
Failure Analysis Services
REQUEST A QUOTEConstellation PowerLabs Brings Over 50 Years in Failure Analysis Experience
Constellation PowerLabs was first established in 1911 as the Philadelphia Electric Company’s main calibration and testing lab. In 1964 PowerLabs began performing failure analyses on mechanical component failures to support coal fire plants and soon after, nuclear plants. After a significant increase in electrical component failures, PowerLabs expanded into electrical failure analysis.
Today, we are proud to provide failure analysis services to an array of different industries to ensure the safety of their employees and facilities. In the last decade alone, Constellation PowerLabs has completed over 3,100 failure analysis projects.
Decades of Failure Analysis Records
With Constellation PowerLabs’ long history of failure analyses, we have archived the failure analysis reports into our online OneLab customer database and internal library. Our highly trained engineers and technicians have access to decades of failure records, reports and data, allowing them to make better informed decisions before the start of their analysis.
Apart from all the failure analysis data we’ve accumulated over the decades, our team also uses the failure rate data captured when components are PQI (Parts Quality Initiative) Parts Tested. We have thousands of parts PQI tested annually to ensure components are performing their critical function. PQI data and testing ensures defective parts are identified before installation, reducing downtime, labor and logistics costs, and yielding substantial parts replacement savings.
Our Process
To understand why a part failed, it takes investigation through observation and collection of data. Our team has a wide array of lab equipment and access to our extensive online database OneLab. This database provides decades of records of past performed failure analysis and valuable insight on past manufacturers and models, thereby enabling us to know what products tend to fail and why before we ever look at the part.
Our qualified engineers and technicians will then perform a series of examinations and testing methods to find the cause of the failure. We provide these services across all industries. Our goal is to quickly analyze the data and provide valuable information based on our findings to determine the root cause so you can identify the true cause of failure and take the right corrective action to prevent recurrence.
Types of Critical Component Failures That Constellation PowerLabs Supports Through Failure Analysis
Types of Parts We Examine:
| Bearing Failure | Switch Failure | Pump Failure | Solenoid Failure |
| Relay Failure | Valve Failure | Weld Failure | Pipe Failure |
| Circuit Board Failure | Diode Failure | Electrical Failure | Gasket Failure |
| Bolt Failure | Transformer Failure | Gear Pump Failure | Insulator Failure |
| Diesel Engine Failure | Metallurgical Failure | Transducer Failure | Pressure Switch Failure |
| Power Supply Failure | Cable Failure | Voltage Regulator Failure | Engine Failure |
Constellation PowerLabs Failure Analysis Services
Apart from the valuable data we have from our decades of experience in failure analysis, we embrace new technologies to allow us great visibility into the reasons behind the failure. These technologies are instrumental in helping our engineers and technicians perform a successful failure analysis.
Material Analysis
SEM (Scanning Electron Microscopy)
SEM (Scanning Electron Microscopy) is a high magnification microscope with magnification ranging from 10 to 200,000. It has a resolution of 5.0 nm at 30 kV. Through the use of electrons, this microscope creates images by scanning the material surface, helping the user determine the composition.
EDS or EDX (Energy Dispersive X-Ray Spectroscopy)
EDS or EDX (Energy Dispersive X-Ray Spectroscopy) is a detector on the SEM. This helps the user view the elemental composition or chemical characterization of the sample.
OES (Optical Emission Spectroscopy)
Operation of this particular spectrometer is based on the principle of the direct-reading atomic emission analytical technique which depends on the fact that atoms of elements can be energized (excited) to emit radiant energy when exposed to a suitable excitation source. When this radiant energy is dispersed it emerges as a light spectrum having a pattern determined by the structure of the atoms that have been excited. Since atoms of different elements contain different electron configurations, each element has a distinct and characteristic spectrum, with spectral lines occurring at different wavelengths. Each element can be identified by its characteristic lines. During quantitative analysis, line brightness represents element concentration in the specimen.
FTIR (Fourier Transformed Infrared Spectroscopy)
This device is used for polymer analysis and oils. This technique provides a spectrum that can be found in each polymer, grease or lubricant. It looks for distinguishing peaks to see if it fits that certain material characteristic.
Wilson Rockwell Hardness Testing Series 500 & Series 2000
This device allows the user to perform hardness testing, where hardness is tested on the level of force required to make a specific dent size in the material. This unit determines the hardness of the material. This technique can be used for polymers, metals and alloys that need to meet a certain standard.
Dimensional Analysis
Creaform HandySCAN Black Elite Series 3D Scanner
This scanner is a non-contact dimensional device that uses lasers. An instrument that analyzes the surface of a component to create a mesh model in CAD or similar modeling software and measure dimensions of the component.
- Accuracy: 0.025 mm (0.0009 in)
- Volumetric accuracy: 0.020 mm + 0.040 mm/m (0.0008 in + 0.0005 in/ft)
- Measurement resolution: 0.025 mm (0.0009 in)
- Part size range (recommended): 0.05 – 4 m (0.15 –13 ft)
Learn more about our HandyScan and how this supports our failure analysis projects.
Keyence Optical Comparator
This is used for dimensional measurements and provides non-contact since it uses light to measure and cast a shadow through the part being analyzed.
Keyence VHX Digital Microscope
This device not only makes 2D measurements but allows the user to make advanced measurements such as particle counting and produce high quality images.
Keyence XM Handheld Probe Coordinate Measuring Machine
It is a handheld coordinate measuring machine (CMM) that measures 3D/GD&T features. It has an accuracy of +/- 8m (8 micrometers).
CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine)
A dimensional measuring device for contact is used to measure a part using coordinate processing technology. This allows the user to retrieve the full dimensions of a component and is often used for more complicated dimensions.
The Benefits of Failure Analysis
Finding out why something failed can lead to positive changes in your operations, from supporting daily production to the overall safety. Here are a few of the benefits your company can experience when you find the root of the cause from a failure analysis:
-
Reduce Costs
There will be less maintenance when identifying the root cause, therefore reducing costs.
-
Safety
Identifying the cause can contribute to not only the safety of the environment, but also allow safer working conditions for employees.
-
Equipment Reliability
When the equipment is used correctly, production can successfully run without causing downtime.
-
Design Changes
When a failure analysis is performed, there can be changes to better the system.
Correcting the Action
In order to prevent this failure from re-occurring, it’s encouraged to develop a corrective action plan. Whether it’s training employees on how to handle the equipment correctly or contacting the manufacturer to make sure they are meeting the design requirements, taking the extra steps necessary to create preventable measures is only for your benefit.
Communication is Key
We work to provide our customers a thorough failure report so they can make the best corrective action to ensure greater equipment reliability and safety within the workplace. Constellation PowerLabs team of experts not only analyze the components before them using some of the latest technologies available, but often communicate with the customers directly for them to successfully complete the failure analysis.